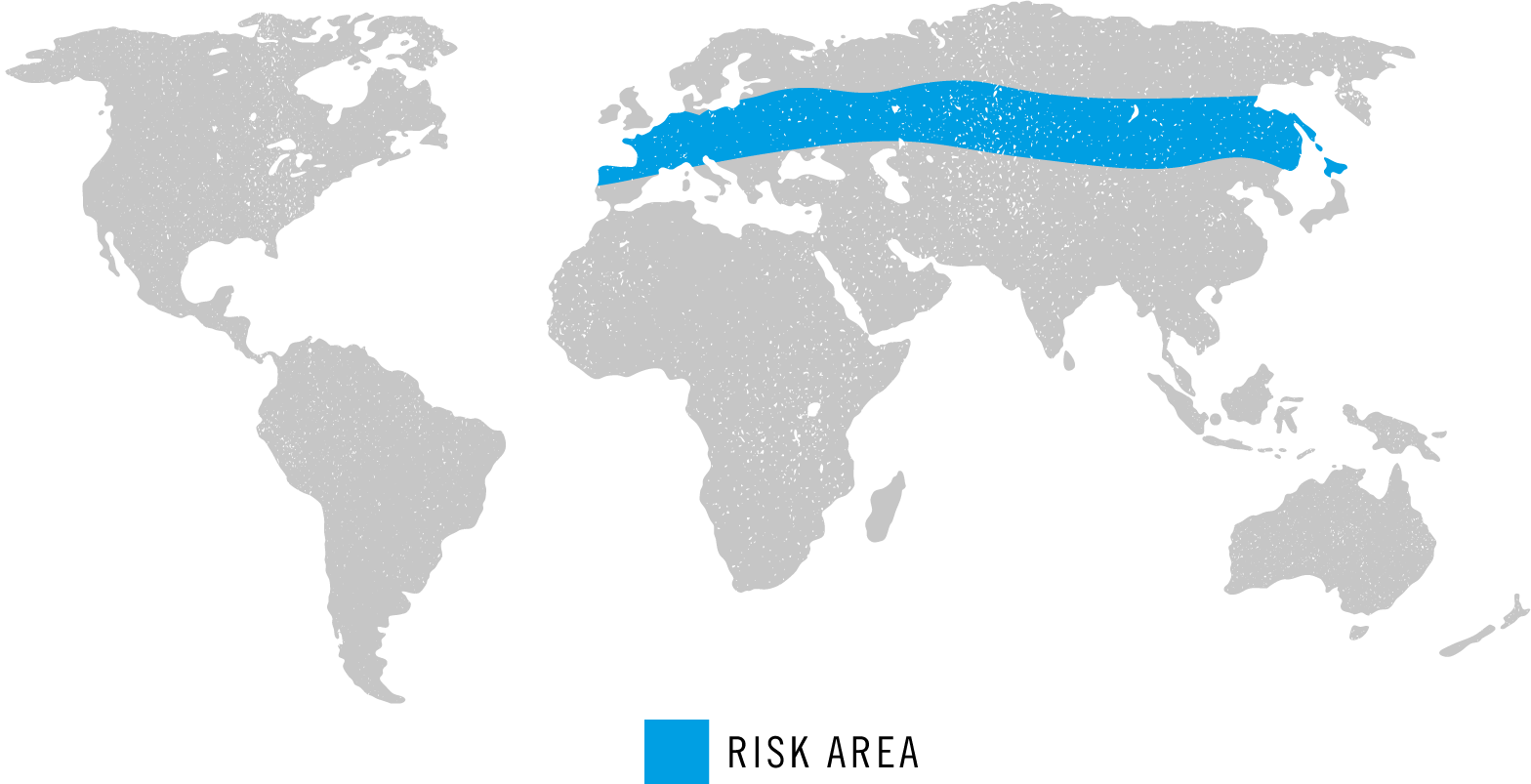
Tick Borne Encephalitis
| Age of Use | Doses Required | Schedule | Time Before Travel | Booster Required |
| 16 years+ | 2 | 0, 1-3 months | Last dose 2 weeks before* | 5-12 months |
Tick Borne Encephalitis Paediatric
| Age of Use | Doses Required | Schedule | Time Before Travel | Booster Required |
| 1-15 years | 2 | 0, 1-3 months | Last dose 2 weeks before* | 5-12 months |
*Vaccines work best if given time to become active. This vaccine can be given up to the day before travel and will provide some cover.
Risk Areas